As of 31st December 2020, the ISO Survey reported approximately 1.5 million organisations with valid Management System (MS) standard certificates globally. In Singapore, there are currently 6158 valid MS standard certificates that cover the area of Quality, Energy, Environmental, Food Safety, Workplace Health and Safety, and Information Security. One of the significant benefits of implementing these MS standards is the improved risk management capabilities to protect businesses and the people and environment.
Implementing these MS standards also reduces the number of global deaths and injuries arising from the negligence or inability to address organisations’ risks. Within most MSs, risks are assessed through a standardised risk management process. Therefore, to effectively implement an MS, knowledge of risk management is crucial for all organisations.
By the end of this article, you will be equipped with knowledge on:
- Risk assessment (Singapore-focused)
- Other areas where risk assessments may be applied to your organisation
- Who, when and how should a risk assessment be conducted
What is risk assessment in Singapore?
Risk assessment in Singapore usually refers to the Ministry of Manpower’s Workplace Safety And Health (Risk Management) Regulations. The regulation requires employers or someone from the top management to manage risks by:
1. IDENTIFYING AND ASSESSING HEALTH AND SAFETY HAZARDS IN THE WORKPLACE

Identifying safety and health hazards is a process where your organisation lists down all possible hazards, whether their sources are within its control. These hazards are risks that usually prevents the organisation from reaching its objectives. An example may be organisations handling highly flammable products that may cause workplace accidents.
The assessment of health and safety hazards is part of the process where organisations conduct risk assessments. This usually involves an evaluation after risk and hazard identification by assigning severity and likelihood scores to determine if further risk control measures must be implemented.
2. CONTROLLING AND MONITORING RISKS
Controlling risks refers to taking all reasonably practicable measures to eliminate or reduce workplace safety and health hazards. These control measures follow the principles of the Hierarchy of Control as seen in the image below.
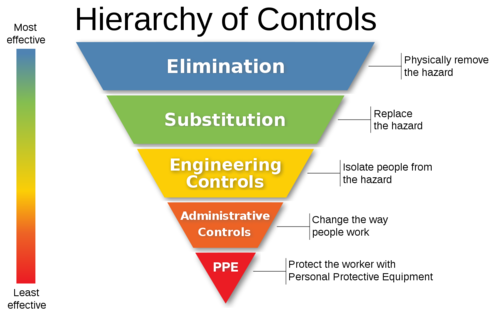
3. COMMUNICATING THE RISK INVOLVED IN THE WORKPLACE TO STAKEHOLDERS
Your organisation’s employer or top management shall ensure that personnel who may be exposed to the identified risks to their health and safety are informed of the nature of risk and also the workplace risk control measures that are put in place.
What are the other areas where risk assessments may be applied to your organisation?
Aside from the context of risk assessment in Singapore which focuses mainly on workplace health and safety, the following are other areas where risk management (inclusive of risk assessment processes) may be applied to your organisation’s business depending on the type of products and services provided.
- Quality Management (ISO 9001, ISO 13485 etc)
- Energy Management (ISO 50001)
- Environmental Management (ISO 14001)
- Food Safety (ISO 22000)
- Information Technology Security (ISO 27001)
Within these areas, the mentioned standards above are most common and available where risk management is an integral part of the implementation.
Who, when and how should a risk assessment be conducted?
Who – In most organisations, risk assessment may be conducted not only by the employer or top management but also by anyone who has experience in risk management. If there is no one within the organisation capable of conducting risk assessment, training courses may be considered for the organisation.
When – Risk assessment should be conducted before and after your organisation rolls out products or services to the customers. Usually, in the design stage, risk assessment have to be conducted.
Similarly, after identifying all possible risks with your product and services, your organisation should be proactive in identifying new risks or hazards that may arise during the production or post-production phases where your organisation’s business is operating live. This is usually called the monitoring stage.
How – Risk assessment is recommended to be conducted in accordance with ISO 31000:2018 – Risk Management Guidelines. This international standard outlines the risk management guidance from risk identification, analysis, evaluation, treatment, monitoring, review, recording to reporting, which can be applied in Singapore’s context of workplace health and safety and the other areas mentioned above.
Conclusion
In conclusion, risk assessment in Singapore mainly focuses on workplace health and safety. Thus, organisations in Singapore usually implements the ISO 45001:2018 – Occupational health and safety management systems – Requirements with guidance for use or the Singapore Standard 506 – Occupational Safety and Health Management System.
These standards have risk management processes required for organisations to implement, ensuring that Singapore’s Ministry of Manpower Regulations is not breached.
This risk assessment standard can help your organisation create a safe, healthy and comfortable work environment for workers, contractors, sub-contractors, visitors and the surrounding community. In turn, it provides a good image for your organisation, projecting it as one that pays attention and maintains occupational health and safety in the organisation.





