In this digital era, many organisations and companies would store, process and exchange information through the internet. Some of the information may be considered sensitive data that require intrusion prevention, for instance, by securing communications via mobile devices and providing security gateways or network security.
Therefore, many organisations and companies face the urge to have proper information storage security and data security in an integrated implementation of an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
The first thing that might come to mind when discussing ISMS is mostly ISO 27001. But do you know that the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have more than 20 guidelines and information security standards published for the ISMS? These documents, including the ISO 27001, are known as the ISO/IEC 27000 series.
In this article, you will learn:
- What ISO 27000 series stands for?
- What are the components of the ISO 27000 series?
- Are all these components of the ISO 27000 series mandatory?
- How to implement ISMS and the advantages for your organisation or company?
What does the ISO 27000 series stand for?
ISO 27000 or ISO/IEC 27000 series, also known as the ISMS family of standards, applies to all types and sizes of organisations or companies that collect, process, store, and transmit information (e.g., government agencies, e-commerce, consulting firms, telecommunications organisations, etc.)
The purpose is to provide requirements and detailed guidance to help organisations and companies to achieve compliance with ISMS and develop information security incident management by implementing information security control based on identified risks of information assets.
What is an information asset?
The term asset in ISO/IEC 27002:2022 is defined as anything that has value to the organisation and company. Therefore information assets are information valuable to organisations and companies. These include intellectual property, personally identifiable information (employee health information, employee details), and information entrusted by customers or interested parties.
Information assets can be presented in digital form (digital documents and records), material form (paper-based documents and records), and in the form of employee knowledge. Nevertheless, information assets have three essential properties:
- Confidentiality – Secrecy level of the information assets, e.g., confidential, for internal use only, accessible to the public
- Integrity – The completeness and accurate state of the information asset
- Availability – Availability of information assets when needed
The value of the information assets is usually evaluated by how much damage or adverse consequences the organisation or company has when those properties are compromised.
What are the components of the ISO 27000 series?
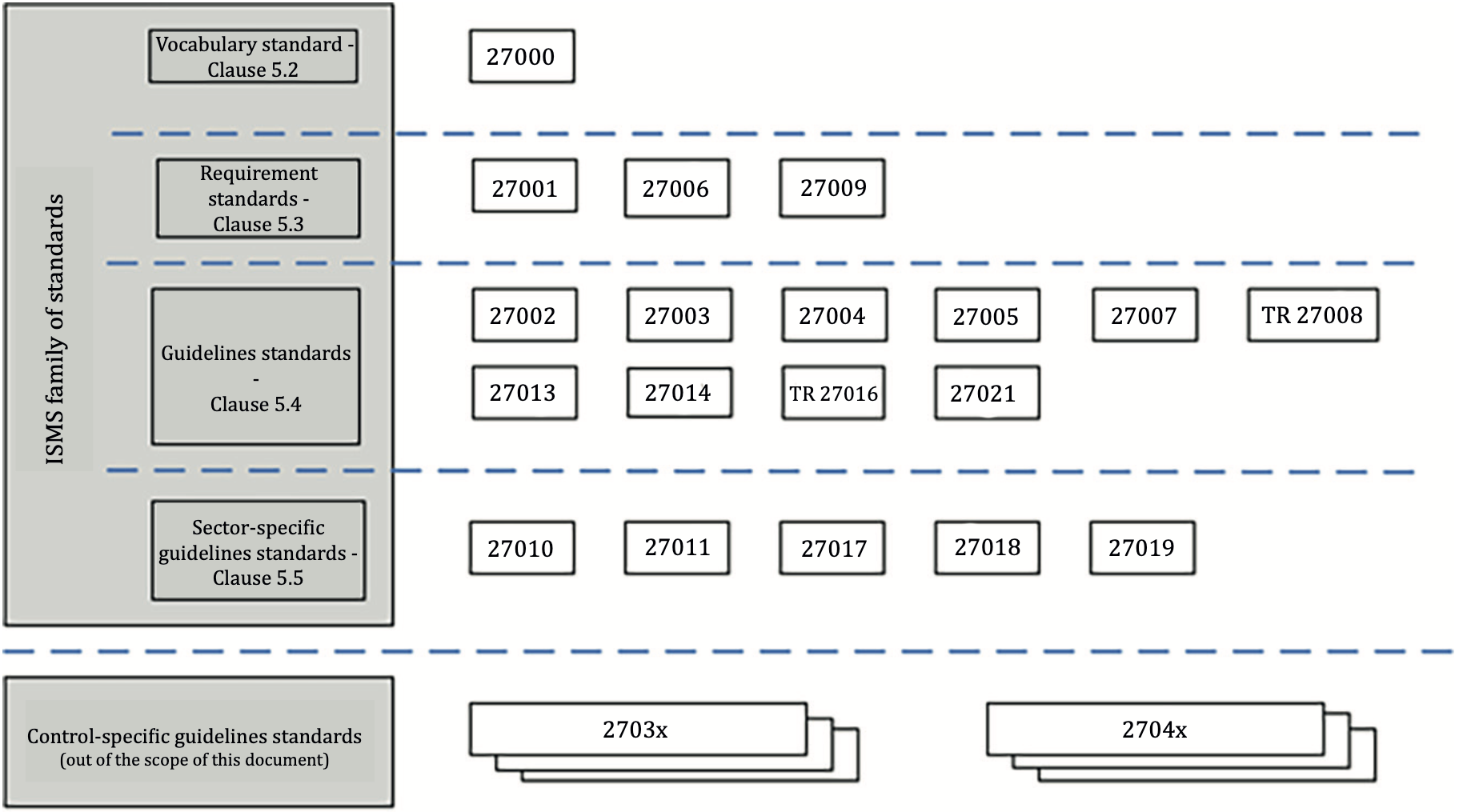
ISO 27000 series consists of many standards, each serving and covering a different scope of ISMS. These standards are categorised into the following three categories:
- Standards describing requirements
- Standards describing general guidelines,
- Standards describing sector-specific guidelines.
From the list of standards, six standards have a significant role in the operation of ISMS in general:
- ISO/IEC 27001 – Information technology – Security techniques – Information security management systems – RequirementsScope: Describes requirements for organisations to implement information security control according to their context of organisations.Purpose: Provide normative requirements for developing and operating information security management systems, including controls.
- ISO/IEC 27002 – Information technology – Security techniques – Codes of practice for information security controlsScope: Describe a list of commonly implemented controls for information security.Purpose: Provide specific advice and guidance on implementing controls based on ISO/IEC 27001.
- ISO/IEC 27003 – Information technology – Security techniques – Information security management – GuidanceScope: Provide explanation and guidance on ISO/IEC 27001.Purpose: Provide guidance to implement information security based on ISO/IEC 27001 successfully.
- ISO/IEC 27004 – Information technology – Security techniques – Information security management – Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and and evaluationScope: Describe guidelines to monitor, measure, analyse, and evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented ISMS.Purpose: Provide a framework to assess the effectiveness of the implemented ISMS based on ISO/IEC 27001.
- ISO/IEC 27005 – Information technology – Security techniques – Information security risk managementScope: Provide guidance for information security risk assessment.Purpose: Provide guidance to implement process-oriented risk management for information security.
- ISO/IEC 27006 (Information technology – Security techniques – Requirements bodies providing audit and certification of information security management systems)Scope: Describe requirements to be practised by certification bodies.Purpose: Provide compliance and support the accreditation of certification bodies.
For standards describing sector-specific guidelines, the scope of each standard will be specialised based on the context of the organisations, such as:
- ISO/IEC 27010 – Information technology – Security techniques -Information security management for inter-sector and inter-organisational communicationsScope: Describe controls and guidelines on initiating, implementing, maintaining, and improving information security in inter-organisational and inter-sector communications.Purpose: To provide trust when exchanging and sharing sensitive information, encouraging the international growth of information-sharing communities.
- ISO/IEC 27017 – Information technology – Security techniques – Code of practice for information controls based on ISO/IEC 27002 for cloud services
 Scope: Provides additional implementation guidance for relevant controls specified in ISO/IEC 27002 that relates explicitly to cloud services for cloud service providers and customers.Purpose: To provide additional cloud-specific implementation guidance based on ISO/IEC 27002 and other controls to address cloud-specific information security threats and risks.
Scope: Provides additional implementation guidance for relevant controls specified in ISO/IEC 27002 that relates explicitly to cloud services for cloud service providers and customers.Purpose: To provide additional cloud-specific implementation guidance based on ISO/IEC 27002 and other controls to address cloud-specific information security threats and risks. - ISO/IEC 27019 – Information technology – Security techniques – Information security controls for the energy utility industryScope: Provides guidance for the energy industry that controls and monitors the production or generation, transmission, storage and distribution of electric power, gas, oil and heat, and controls associated supporting processes.Purpose: To ensure that in the process control domain of the energy utility industry, adequate information security is achieved through the implementation and continuous improvement of an ISMS following ISO/IEC 27001.
- ISO/IEC 27701 Security techniques – Extension to ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002 for privacy information management – Requirements and guidelines
 Scope: To provide guidance on implementing a privacy information management system.Purpose: ISO/IEC 27701 is an extension to ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 that provides additional guidance on processes and security controls for organisations handling personally identifiable information (PII).
Scope: To provide guidance on implementing a privacy information management system.Purpose: ISO/IEC 27701 is an extension to ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 that provides additional guidance on processes and security controls for organisations handling personally identifiable information (PII).
In addition, the ISO and IEC also published ISO/IEC 27000. The function is to provide an overview of the ISMS family of standards and terms and definitions used in the ISMS.
Is the ISO 27000 series mandatory?
Although ISO 27000 series consists of many standards, only some are binding. The only standard that we can get a certification against is ISO 27001. This is because ISO 27001 contains the normative requirements for developing and operating information security management systems, including a list of controls to protect information assets.
Another standard which contains requirements is ISO/IEC 27006. Yet, unlike ISO/IEC 27001, which is made for organisations or companies, ISO/IEC 27006 is made for certification bodies that provide ISMS certification. ISO/IEC 27006 is used to demonstrate the competency and reliability of the certification bodies.
How to get started with ISMS?
The first step is to analyse your organisation’s current management system against ISO 27001. With this gap analysis, your organisation can determine what ISMS requirements were not covered by your existing system.
Next, your organisation can work its way up from the identified gaps. The next step is to determine the appropriate controls for information security based on ISO 27001 to protect your information assets from being compromised.

The controls for information security specified by ISO 27001 are mainly categorised as follows:
- Information security policies
- The organisation of information security
- Human resource security
- Asset Management
- Access control
- Cryptography
- Physical and environmental security
- Operations security
- Communications security
- System acquisition, development and maintenance
- Supplier relationships
- Information security incident management
- Information security aspects of business continuity management
- Compliance
The compromise of information assets is caused by threats (potential cause or risk of an unwanted incident that is harmful to organisations or companies, e.g., cyber attack, natural disaster) and their corresponding vulnerabilities (gap in current security system which is penetrable by a threat).
When there is a threat without a corresponding vulnerability and vice versa, it is considered that there is no risk that could compromise the information asset. On the other hand, the presence of threats and vulnerabilities indicates a risk to information assets. Therefore, organisations and companies must take security measures to protect their information assets using risk assessment.
Information security risk assessment
Risk assessment is done by identifying all assets and defining their value, then identifying their threats and vulnerabilities and implementing a suitable security control. It is essential to determine the acceptance criteria for threats and vulnerabilities to apply appropriate controls.
The controls include policies, procedures, rules, organisational structure and functions for software and hardware. These controls aim to protect the information assets.

The security controls are managed in the ISMS. Like other management systems, such as ISO 9000 series (management systems for quality assurance) and ISO 14000 series (environmental protection management), organisations or companies have to maintain, monitor, review and make improvements as necessary to their implemented controls to achieve an effective system.
Other key principles contributing to the success of ISMS are continuous feedback, promotion of awareness for information security and incorporation of management commitment and the stakeholder’s interest.
The benefits of an Information Security Management System
Information security is relevant to your organisation or company, your clients or interested parties and your government. Implementing the ISMS into your organisation or company will protect your information assets from security incidents such as data breaches and cyber attacks.
ISMS implementation will also save your organisation or company from further problems due to information security incidents (e.g. financial loss, legal actions, personal consequences, business disruption and negative impression of your organisation’s name and reputation etc.).
It also provides privacy protection to protect personal health information and other identifiable information.

Additionally, implementing ISMS will boost the confidence of your clients and interested parties in doing business with your organisation or company by demonstrating your commitment to information security and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
To sum up, saving and exchanging information through the internet is part of daily business in the present days. This information is a valuable asset to the organisation and company. Consequently, information security has become a big concern for many organisations and companies. Thus many of them are adopting and incorporating ISMS into their business.
While ISO 27001 is arguably the most popular standard for ISMS published by the ISO and IEC, more than 30 other standards provide requirements and guidelines for the implementation of ISMS.
These standards are known as the ISMS family of standards or ISO 27000 series. The standards in the ISO 27000 series can be categorised into three groups based on their purposes.
ISO 27001 specifies normative requirements for organisations and companies in establishing and implementing their ISMS. This is the only standard from the ISO 27000 series for which organisations and companies can be audited and certified. In contrast, other standards complement the ISO 27001 requirements for information assets security.

Implementation of information security is beneficial not only for your organisation or company but also for your interested parties and clients. For instance, it will protect confidential data, demonstrate quality management and standards for information security to your interested parties and clients, and help avoid consequences damaging the reputation of your organisation or company and your business continuity.





